Inside the Honor of Kings Esports Partnership Model: How Eight Teams Earned a Spot in Major Leagues
Even before its June 2024 global release, Honor of Kings has been investing strongly in its esports ecosystem. Level Infinite has said that it has committed $15 million for the 2025 esports roadmap, something which it did last year as well.
For 2025, though, there is one ‘major’ (pun intended) change, and that is through the Honor of Kings Major League, or as it’s being abbreviated – the KME in the East and KMW in the West. It features two editions in the East and the West, but the biggest addition is that both of them will have four partnered teams each – a system where certain teams get guaranteed slots.
Besides the Major League, Honor of Kings has regional competitions in Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Brazil, and a Wildcard league for other SEA countries. Furthermore, there is an Open and Campus series for the grassroots. These along with three international tournaments throughout 2025 round up its $15 million investment.
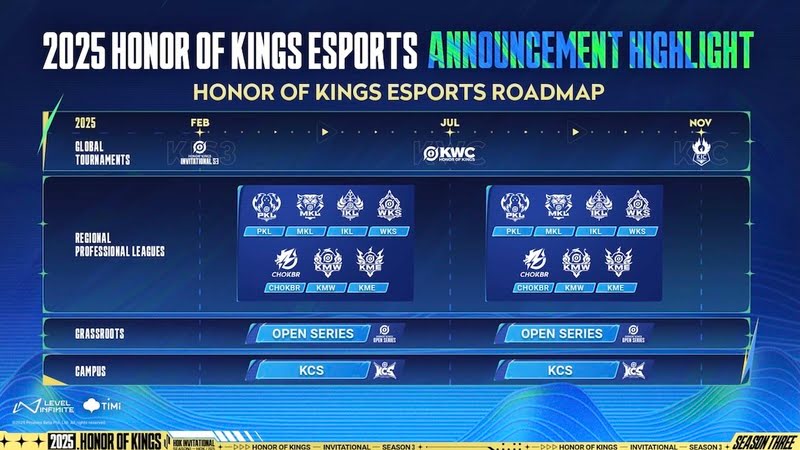
Image Credits: Level Infinite
What is the Honor of Kings esports partnership model?
Level Infinite bringing a partnership model for esports isn’t new, as the PUBG Mobile Super League (PMSL) also follows something similar. These partnered teams in the KME and KMW get guaranteed slots, and unlike a franchise league, didn’t have to pay a buy-in amount to be a part. Instead, they had to go through a selection process before they were shortlisted.
A franchise esports league may seem great on paper, as teams get more revenue avenues and increased visibility, while players also receive better stability — but this isn’t always good. While the King Pro League (KPL) in China has seen a lot of success through a franchised model, the Overwatch League (OWL), which shut down its franchised model in 2023, is an example of the repercussions of not properly building the ecosystem before getting teams to make a huge financial commitment.

Image Credits: Level Infinite
James Yang, the Senior Director of Level Infinite Global Esports Center, told Esports.net that a franchise model isn’t something that they want to build yet.
“I don’t think we want to go for a very crude franchise system, because we want our Pro League to remain open — where anyone can play, anyone can have a chance to rise and eventually be promoted to global tournaments.”
Who are the 8 teams in the Honor of Kings esports partnership program?
The lucky 8 who have been selected for the inaugural Honor of Kings Major League are 9z Team, Next Ruya, OG, and Virtus.pro for the West league (KMW). The Eastern league (KME) has Crazy Raccoon, Gen.G Esports, Nongshim RedForce, and R8 Esports as partnered teams. Both of them have 3 slots through open qualifiers.
The Factors That Go Into Selection
Yang told us that there are various factors that were considered when selecting teams — from brand name and competitiveness to team management.
Obviously, getting these esports organizations — who each command loyal fans — to invest in Honor of Kings will not only support the ecosystem but also encourage new players to engage with the game.
“We also look at how they can support us — some teams have a large following or strong media power, which makes it mutually beneficial.”

Image Credits: Level Infinite
Besides that, competitiveness and team management are other important aspects. Honor of Kings wants to showcase the pinnacle of mobile MOBA esports, and the only way to achieve that is by constantly building talent.
“We wanted to work with strong teams — teams that can invest more into HOK. So for all the teams we’ve selected so far, we are checking their competitiveness: whether they can build a strong roster to compete against other regions and other teams. Another factor is team management. Some teams don’t manage their players well, while others are very supportive in helping their players grow their skills.”
The partnership model allows teams to get guaranteed slots in the league, offering them a higher chance to compete internationally. The winners of the West and East editions will both get a slot in the Honor of Kings World Cup (KWC) 2025 happening at the Esports World Cup (EWC) in Riyadh.

Image Credits: Level Infinite
For teams like Gen.G Esports and Virtus.pro, the KWC is even more important as they are also competing for the Esports World Cup Club Championship 2025, which has a prize pool of $27 million.
Yang said that they want to look at the partnership model from a long-term perspective. For now, it seems that besides guaranteed slots, teams aren’t getting any financial incentives (they are guaranteed a minimum $6,000 from the prize pool). However, this could change as the league matures.
“It’s a bit early to talk about exact financial support for the teams. But yes, we’re approaching this as a long-term partnership. If there’s an opportunity to offer more support in the future, we’ll definitely do it. As for the detailed plans and how we’ll implement them — it’s still too early to share. But that is the direction we want to go in.”
The spring season of the KME and KMW will begin on April 17. Both leagues are taking place offline in Malaysia with prize pools of $50,000 on the line. Fans can tune into the action live on the Honor of Kings global esports YouTube channel.